Acceleration Due To Gravity Example Problems
M g m g m m r m 2 on the surface of mars simplify to obtain g m g m r m 2.
Acceleration due to gravity example problems. But at large distances from the earth or around other planets or moons it is varying. Near the surface of earth the acceleration due to gravity is approximately constant. G universal constant m earth. It explains the concept of acceleration due to gravity.
The formula of newton s second law of motion. We refer to this special acceleration as the acceleration caused by gravity or simply the acceleration of gravity. What is the acceleration due to gravity at the moon s surface. Moon s mass 7 35 x 10 22 kg the radius of the moon is 1 7 x 10 6 m universal constant is 6 67 x 10 11 n m 2 kg 2.
Acceleration due to gravity formula. The above formula shows that the value of acceleration due to gravity g depends on the radius of the earth at its surface. Here are some practice questions that illustrate this concept. The acceleration is due to the universal force of gravity therefore newton s second law and the universal force of gravity are equal.
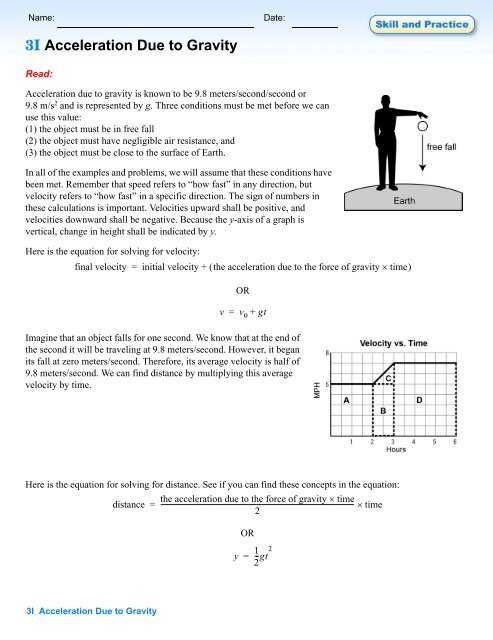
The acceleration which is gained by an object because of gravitational force is called its acceleration due to gravity its si unit is m s 2 acceleration due to gravity is a vector which means it has both a magnitude and a direction the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of earth is represented by the letter g it has a standard value defined as 9 80665 m s 2 32 1740 ft s 2. Air resistance may be ignored. Free falling objects are falling under the sole influence of gravity. The brick strikes the ground in 2 50 sec.
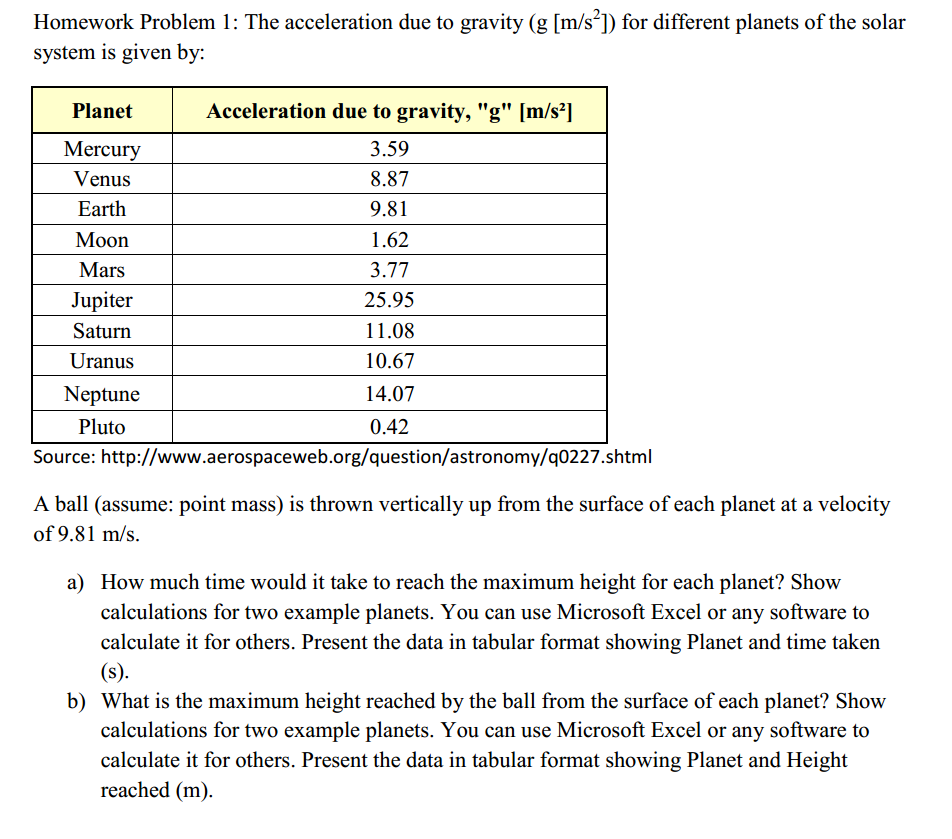
Practice questions researchers at nasa load a 100 kilogram package onto a rocket on earth. The acceleration due to gravity depends on the terms as the following. A if a mango of mass kg falls from a tree from a height of 15 meters what is the acceleration due to gravity when it begins to fall. This force causes all free falling objects on earth to have a unique acceleration value of approximately 9 8 m s s directed downward.
Let the gravitational field strength on mars be g m and that of earth be g and m be the mass of the object. This physics video tutorial focuses on free fall problems and contains the solutions to each of them. The formula of newton s law of universal gravitation. Solution to problem 4.
Ignore air resistance for all problems. Mass of the body distance from the center of mass constant g. Calculate the value of g in the following two cases. Acceleration due to gravity problems and solutions.
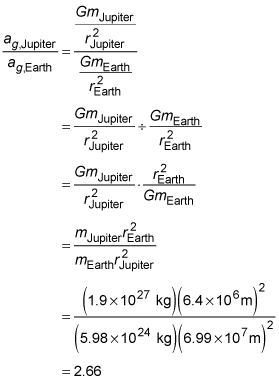
Acceleration due to gravity. The value of acceleration due to gravity is 10 m second second which is calculated by using formula given below. Using physics you can compare the acceleration due to gravity of two different revolving objects.