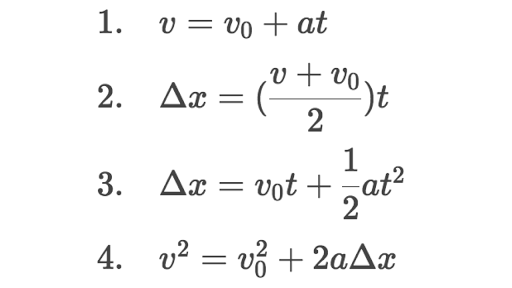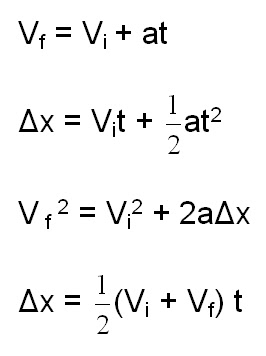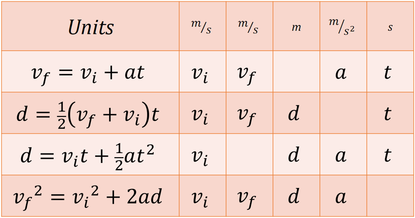Kinematic Equations Acceleration Due To Gravity
If values of three variables are known then the others can be calculated using the equations.
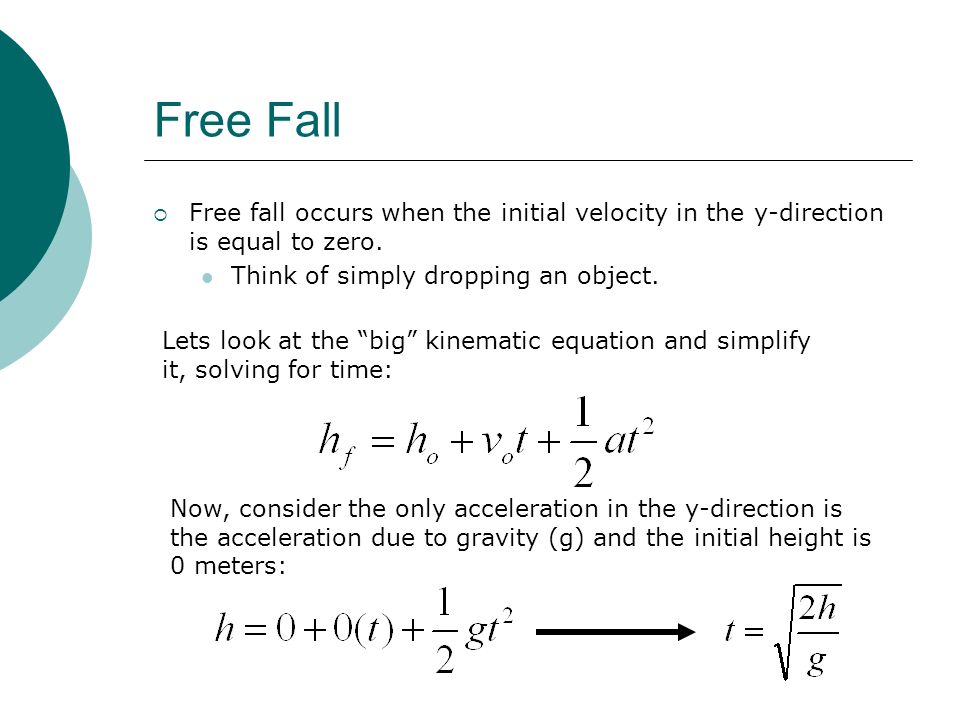
Kinematic equations acceleration due to gravity. The magnitude of this accelation is represented by the symbol g and has the value of 9 8 m s 2. The variables include acceleration a time t displacement d final velocity vf and initial velocity vi. Free fall motion is the motion of an object accelerating due to gravity alone in the absence of air resistance. S ut 1 2 at 2 v u at however the equations are usually rewritten as y ut 1 2 gt 2 v u gt.
The variables include acceleration a time t displacement d final velocity vf and initial velocity vi. Each equation contains four variables. Near the surface of earth the acceleration due to gravity is approximately constant. The use of y instead of s is just to emphasise that we are dealing with vertical motion.
Acceleration due to gravity formula. This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and accompanying. Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Further this acceleration is the same for any falling object.
But at large distances from the earth or around other planets or moons it is varying. However the acceleration value near the earth s surface is known. The acceleration due to gravity depends on the terms as the following. It explains the concept of acceleration due to gravity.
The most common equations we use are. Mass of the body distance from the center of mass constant g. If values of three variables are known then the others can be calculated using the equations. Kinematic equations part 3 adds acceleration due to gravity to the concepts we know and provides further examples of solving related problems.
We can use the same suvat equations as before to solve problems involving acceleration due to gravity. This physics video tutorial focuses on free fall problems and contains the solutions to each of them. Each equation contains four variables. Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another.
Galileo galilei 1564 1642 made quantitative studies to find that the acceleration due to gravity is constant during the fall.