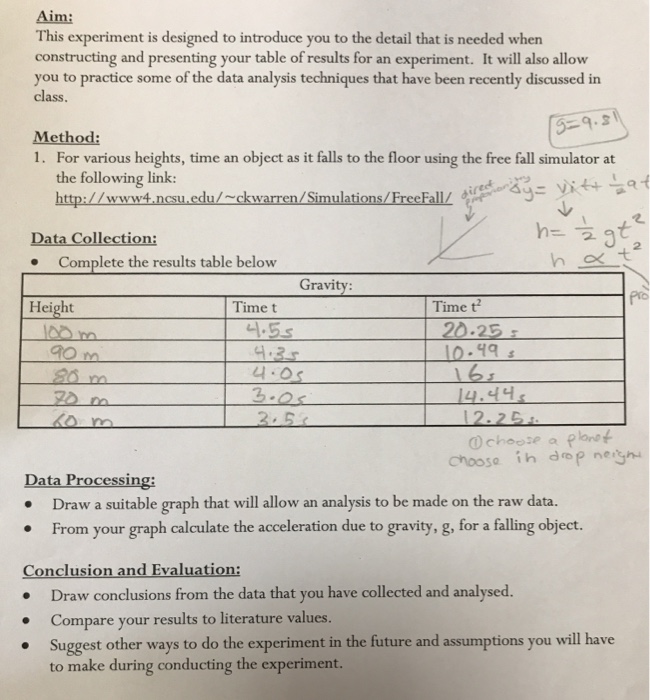
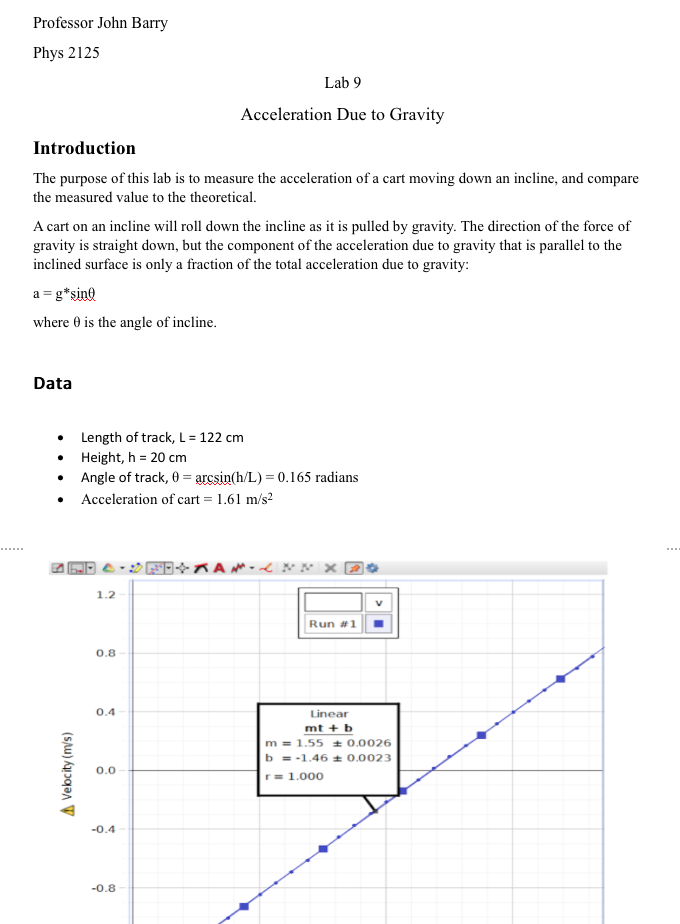
Acceleration Due To Gravity Lab Report Conclusion

The slope is determined.
Acceleration due to gravity lab report conclusion. Gislason the purpose of this motion lab was to find the acceleration of a steel marble going down a straight track six different times to figure out how an object s mass affects acceleration it doesn t due to newton s second law of motion. Get a verified writer to help you with acceleration lab conclusion. Conclusion to motion lab kerreon wright 3rd period ms. Conclusion the small angle approximation model which gives g as being proportional to t2 and l was supported by the data taken using a simple pendulum.
In figure 1 we plot all the data in this way along with the best linear fit to the data. In the conclusion this lab seems to didn t have generated strong support for the theories and hypothesis that g cacm so. 9 90 m s2 accepted value of acceleration due to gravity. The slope of the graph is acceleration due to gravity.
Measured acceleration due to gravity. The measured value of the acceleration due to gravity was quite good only 1 02 larger than the accepted value of 9 80 m s2. This experiment is to measure acceleration on a freely falling object assuming the only force acting on the object is gravitational force. Hire verified writer 35 80 for a 2 page paper.
The slope of this line is acceleration due to gravity. 0 77429 and an r square value. This indicates that our experimental value was close to the true value of gravity on. This is a lab report done by a student and uploaded for educational purposes.
Conclusion the experiment is to calculate the acceleration of gravity using the smart timers. The residual of the data showed that it was a good t for a linear model and the least squares linear t of the data had t parameters of chi squared. 3 results and discussion inspection of equation 2 shows that the free fall distance h depends linearly on the 1 2t 2. The value obtained from the average time squared values yielded a value of a 9 78m s 2 with a discrepancy value of 0 204.
The purpose of the experiment was to measure and confirm the acceleration due to gravity by timing a free falling ball. Gravity and friction also affect the speed of the marble. Although the marble only has a change in speed and not direction we can still determine that acceleration occurred due to the definition. 7 88 m s squared 6 78 m s.
This experiment was done in order to measure gravitational acceleration using simple pendulum. Instead of the acceleration being 9 81 m s 2 down as i hypothesized it was actually 6 73 m s 2 down when calculated due to calculation and experimental errors. There were six different accelerations for each trial and they are. My hypothesis was only partially correct.
Theory all dense objects in free fall have the same acceleration which is known as the acceleration due to gravity the value of acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9 80 m s2. Lab report on measuring gravitational acceleration free download as word doc doc docx pdf file pdf text file txt or read online for free. 9 80 m s2 percent difference.