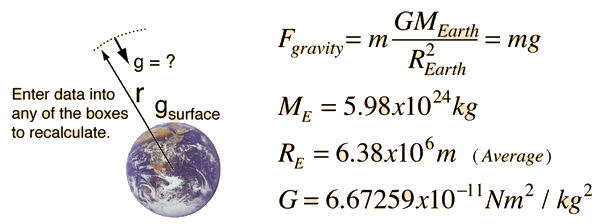Acceleration Due To Gravity Equation

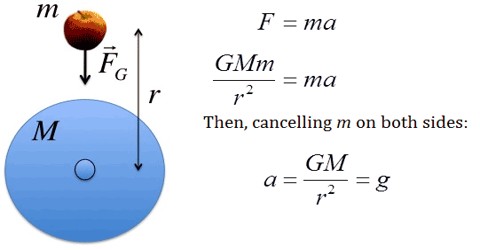
From equations 1 and 2 we get mg gmm r 2.
Acceleration due to gravity equation. For the mass attraction effect by itself the gravitational acceleration at the equator is about 0 18 less than that at the poles due to being located farther from the mass center. Where f is the force acting on the body g is the acceleration due to gravity m is mass of the body. 3 on substituting equation 2 and 3 in equation 1 we get acceleration due to gravity force mass 1. Or g g m r 2.
Or g m 1 l 1 t 2 m 1 l 0 t 0 1. The 2 formulas we will derve for g acceleration due to gravity on the earth s surface are. In this post we will list down and derive the formula of acceleration due to gravity on the earth s surface in other words we will derive the formula or equation of g on the earth s surface. Therefore the acceleration due to gravity g is given by gm r 2.
G gm r 2 and g 4 3 π r ρ gso let s start with the step by step derivation process. Formula of acceleration due to gravity. Free falling objects are falling under the sole influence of gravity. The above formula shows that the value of acceleration due to gravity g depends on the radius of the earth at its surface.
Acceleration due to gravity formula. This is the relation between gravitational constant and acceleration due to gravity. Force acting on a body due to gravity is given by f mg. The value of acceleration due to gravity is 10 m second second which is calculated by using formula given below.
According to the universal law of gravitation f gmm r h 2. This force causes all free falling objects on earth to have a unique acceleration value of approximately 9 8 m s s directed downward. G 1 620 m s 2. The mass of the earth is 5 98x 10 24 kg.
1 dimensional formula of the mass m 1 l 0 t 0. This is the expression of g on the surface of the earth. We refer to this special acceleration as the acceleration caused by gravity or simply the acceleration of gravity. The formula for the acceleration due to gravity is based on newton s second law of motion and newton s law of universal gravitation.
2 also the dimensions of force m 1 l 1 t 2. When the rotational component is included as above the gravity at the equator is about 0 53 less than that at the poles with gravity at the poles being unaffected by the rotation. Acceleration due to gravity g force mass 1.