Variation Of Acceleration Due To Gravity Graph

The atmospheric pressure in the room remains 1 105 pa.
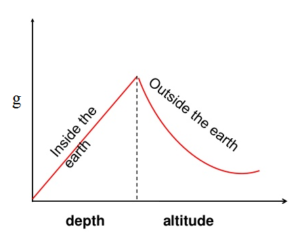
Variation of acceleration due to gravity graph. The kinetic energy time graph of the particle. If g is the acceleration due to gravity at depth d let the earth be of uniform density r and its shape be a perfect sphere. Altitude above the earth s surface. This force causes all free falling objects on earth to have a unique acceleration value of approximately 9 8 m s s directed downward.
Variation of g with height. The radius r h of a black hole is the radius of a mathematical sphere called the event from events inside the event horizon cannot reach the outside world. Suppose the you wish to study a black hole near it at a radial distance of 5 0 r h. Therefore acceleration due to gravity decreases with increase in depth.
The variation of acceleration due to gravity g with distance d from centre of the earth. We refer to this special acceleration as the acceleration caused by gravity or simply the acceleration of gravity. The shape of the earth. If ni and n f are the.
So the graph showing variation of acceleration due to gravity and height would be. In si units this acceleration is measured in metres per second squared in symbols m s 2 or m s 2 or equivalently in newtons per kilogram n kg or n kg 1. Variation of g with height or how acceleration due to gravity changes with height. Variation in acceleration due to gravity g with depth by admin in ask physics cbse physics class xi gravitation interesting questions on september 14 2012.
The temperature of an open room of volume 30 m 3 increases from 17 c to 27 c due to sunshine. Free falling objects are falling under the sole influence of gravity. According to einstein s general theory of relativity r h 2 g m c 2 where m is the mass of the black hole and c is the speed of light. Where r is the density of the earth comparing g and g.
The gravity of earth denoted by g is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation from mass distribution within earth and the centrifugal force from the earth s rotation. Rotational motion of the earth. Here g1 is the acceleration due to gravity at height h and r is the radius of the earth. This is expressed by the formula g1 g 1 2h r.
The value of acceleration due to gravity g is affected by.