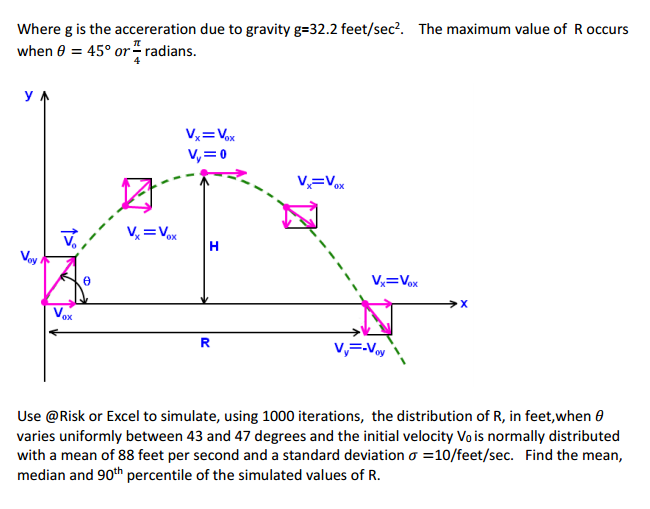
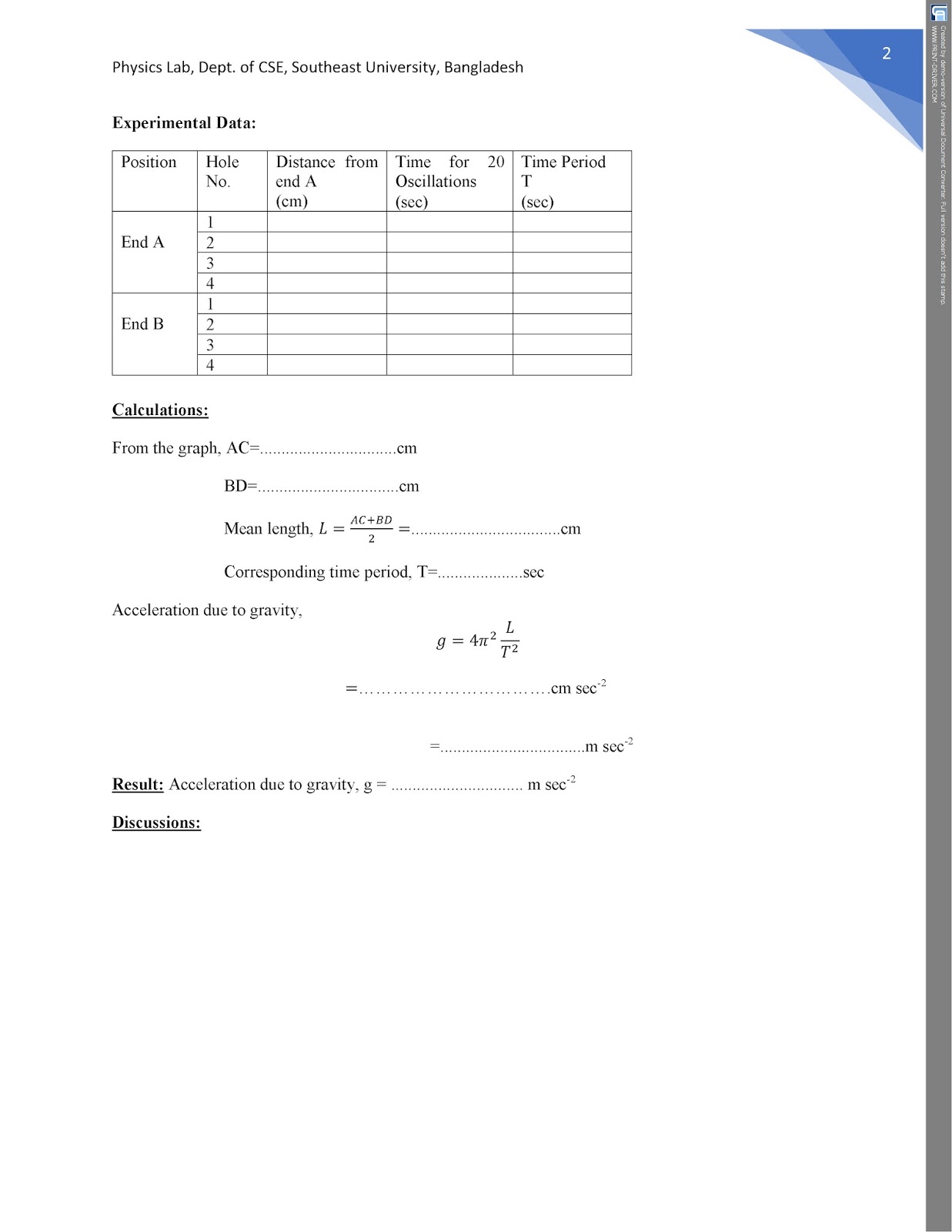
Value Of G Acceleration Due To Gravity

The value of g is more at equator and less at poles.
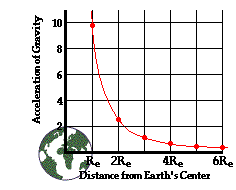
Value of g acceleration due to gravity. Then click the submit button. Select a location from the pull down menu. We define the acceleration due to gravity as the constant acceleration produced on the body when it freely falls under the effect of gravity. For an object placed at a height h the acceleration due to gravity is less as compared to that placed on the surface.
We represent acceleration due to gravity by the symbol g. Important conclusions on acceleration due to gravity. What is acceleration due to gravity. That is to say the acceleration of gravity on the surface of the earth at sea level is 9 8 m s 2.
In the first equation above g is referred to as the acceleration of gravity. When discussing the acceleration of gravity it was mentioned that the value of g is dependent upon location. Image will be uploaded soon. The value of the acceleration of gravity g is different in different gravitational environments use the value of g widget below to look up the acceleration of gravity on other planets.
As depth increases the value of acceleration due to gravity g falls. Thus it is a vector quantity. The above formula shows that the value of acceleration due to gravity g depends on the radius of the earth at its surface. Its value is 9 8 m s 2 on earth.
Let us say a body of mass m is placed at distance r from the earth whose mass is m. Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration that is gained by an object due to the gravitational force. The value of acceleration due to gravity is 10 m second second which is calculated by using formula given below. In si units this acceleration is measured in metres per second squared in symbols m s 2 or m s 2 or equivalently in newtons per kilogram n kg or n kg 1.
It has a magnitude as well as direction. Its standard value on the surface of the earth at. The standard acceleration due to gravity or standard acceleration of free fall sometimes abbreviated as standard gravity usually denoted by ɡ 0 or ɡ n is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the earth it is defined by standard as 9 806 65 m s 2 about 32 174 05 ft s 2 this value was established by the 3rd cgpm 1901 cr 70 and used to.