Value Of Acceleration Due To Gravity Of Earth Is Maximum

The above acceleration is due to the gravitational pull of earth so we call it acceleration due to gravity it does not depend upon the test mass.
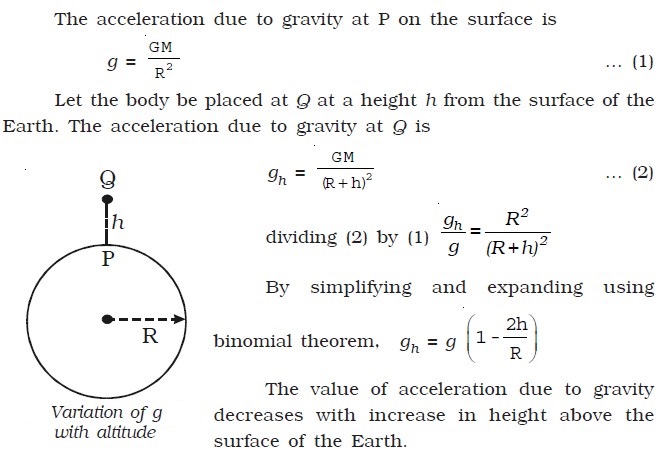
Value of acceleration due to gravity of earth is maximum. This is expressed by the formula g1 g 1 2h r. The graph will be the same for g as we have drawn for overrightarrow e. The value of acceleration due to gravity is 10 m second second which is calculated by using formula given below. The above formula shows that the value of acceleration due to gravity g depends on the radius of the earth at its surface.
The average value of g on the surface of the earth is around 9 8 m s 2. The standard acceleration due to gravity or standard acceleration of free fall sometimes abbreviated as standard gravity usually denoted by ɡ 0 or ɡ n is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the earth it is defined by standard as 9 806 65 m s 2 about 32 174 05 ft s 2 this value was established by the 3rd cgpm 1901 cr 70 and used to. Image will be uploaded soon value of g on earth. G frac gm e r e.
G is maximum at the surface and decreases with the increase in the distance from the earth. Formula of acceleration due to gravity. The gravity of earth denoted by g is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation from mass distribution within earth and the centrifugal force from the earth s rotation. As altitude or height h increases above the earth s surface the value of acceleration due to gravity falls.
The value of g is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of. Variation of g with height or how acceleration due to gravity changes with height. We know that formula for the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth is. Therefore the acceleration due to gravity g is given by gm r 2.
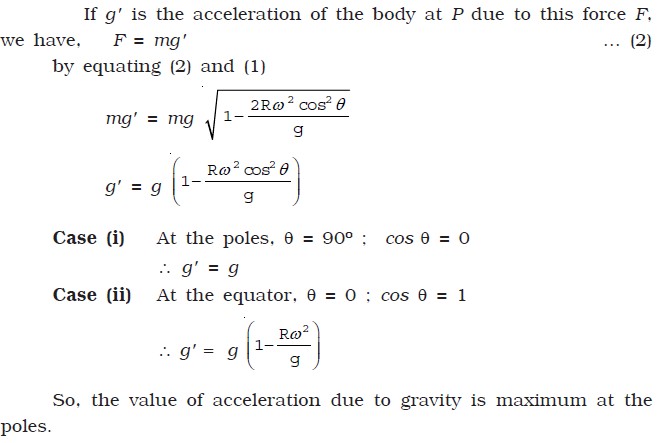
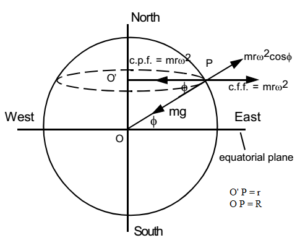
In si units this acceleration is measured in metres per second squared in symbols m s 2 or m s 2 or equivalently in newtons per kilogram n kg or n kg 1. For example the acceleration due to gravity would be different on the moon as compared to the one here on earth. The resulting acceleration is weakest at the equator and maximum at the poles with a difference in magnitude of about 0 5 because the outward centrifugal force produced by rotation is larger at the equator than at the poles. Here g1 is the acceleration due to gravity at height h and r is the radius of the earth.