Table Krejcie And Morgan 1970
The krejcie and morgan 1970 table was chosen because the calculation for.
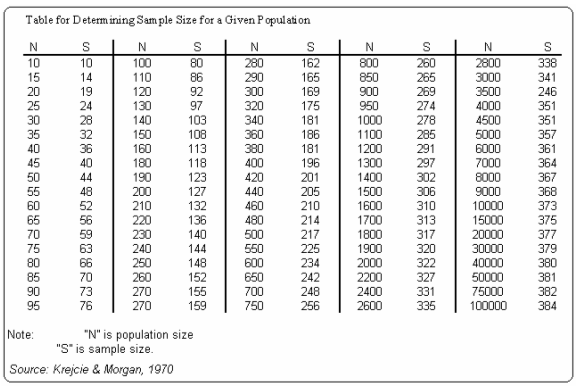
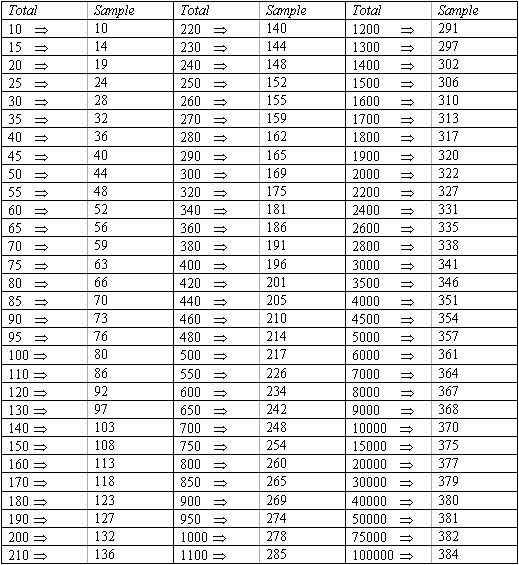
Table krejcie and morgan 1970. Krejcie r v morgan d w. Krejcie and morgan s sample size determination table population sample 10 10 15 14 20 19 25 24 30 28 35 32 40 36 45 40 50 44 55 48 60 52 65 56 70 59 75 63 80 66 85 70 90 73 95 76 100 80 110 86 source. Adapted from krejcie and morgan 1970 3 4 1 exclusion criteria. Concise table of three place probabilities of the symmetric binomial cumulative distribution fo.
Educational and psychological measurement 1970 30. Krejcie and morgan s 1970 developed the formulas for determining the sample size for categorical types of data. The ever increasing need for a representative statistical sample in empirical research has created the demand for an effective method of determining sample size. Educational and psychological measurement 30 607 610.
Krejcie university of minnesota duluth daryle w. This preview shows page 3 5 out of 5 pages. Krejcie and daryle w. The study employed stratified and simple random sampling strategies.
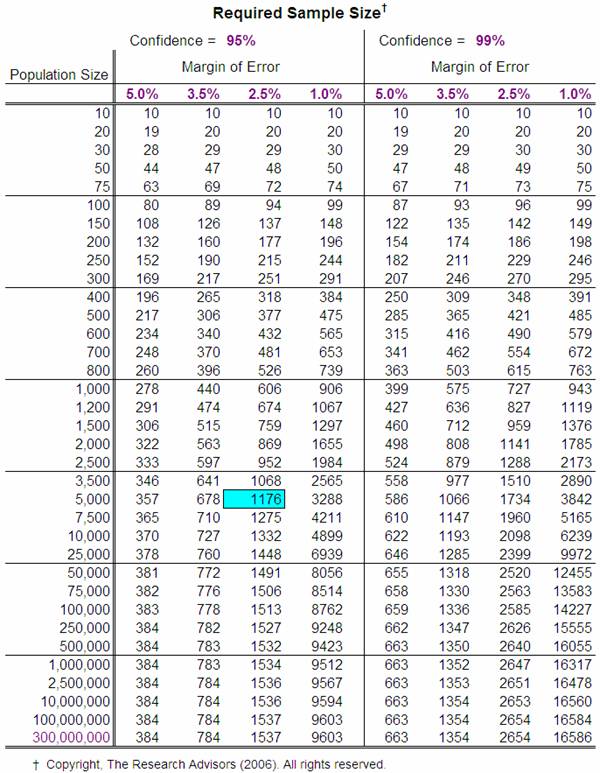
Determining sample size for research activities. Krejcie and morgan 1970 have produced a table for determining required sample size given a finite population. Sample size estimation using krejcie and morgan and cohen statistical power analysis. The table is applicable to any population of a defined finite size.
Stratified sampling grouped school according to county town council and simple random sampling was used to select schools from each. Determining sample size for research activities robert v. The krejcie and morgan 1970 table was chosen because. These formulas for determining the sample size provide identical sample sizes in cases where the researcher adjusts the tabulated value based on the size of the population which should be less than or equal to 120.
Krejcie and morgan 1970 table for determining sample size as cited in amin 2005. Articles citing this one. University the ever increasing demand for research has created a need for an efficient method of determining the sample size needed to be representative of a given population.