Royal British Bank V Turquand 1856 6 El Bl 327

110 on a bond signed by two directors under the seal of the company whereby the.
Royal british bank v turquand 1856 6 el bl 327. In the royal british bank v turquand 1856 1856 engr 470. It has since been codified in section 19 of the ontario business corporations act the obca which provides as follows. 7 8 vict. 6 el bl 327 it was held that a third party was bound to read the company s articles but no more.
Royal british bank v turquand 1856 6 e b 327 is a uk company law case that held people transacting with companies are entitled to assume that internal company rules are complied with even if they are not. The court held that the contract was valid even though. This indoor management rule or the rule in turquand s case is applicable in most of the common law world. England and wales this case cites.
Turquand 1856 119 e r. The rule in royal british bank v. 3 business corporations act rso 1990 c b16. 2 royal british bank v turquand 1856 6 el bl 327.
4 canada business corporations act rsc 1985 c c 44. 2 in the present case the author of the letter in question was the finance and administration manager of the defendant and one would generally expect a person holding that position to write such letters on behalf of the company. Royal british bank v turquand 6 ellis and blackburn 327 119 er 886 report date. Appeal from the royal british bank v turquand 2 jun 1855 1855 engr 531 1855 5 el and bl 248 1855 119 er 474.
Royal british bank v turquand 1856 6 el bl 327 and read no v sager s motors pvt ltd 1970 1 sa 521 ra applied. This principle was authoritatively laid out in royal british bank v. 1856 tuesday may 1st 1856. If such a person honestly and without reason for suspicion thinks that the director with whom he negotiates is authorised to act for the company the company will normally be bound by the director s act under the rule in royal british bank v.
4 canada business corporations act rsc 1985 c c 44. 2 royal british bank v turquand 1856 6 el bl 327. It originally mitigated the harshness of the constructive notice doctrine and. Turquand 1856 6 e.
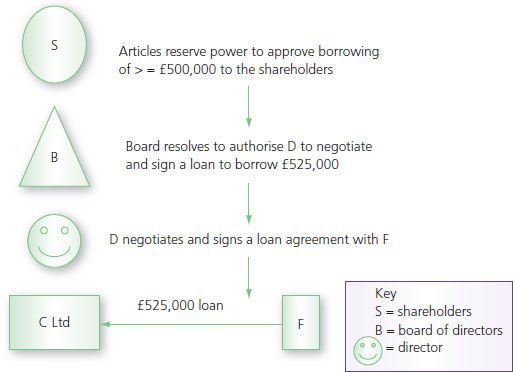
1856 6 e and b 327 1856 engr 470 1856 6 el and bl 327 1856 119 er 886 links. The board borrowed money from the bank via a contract bearing the company s seal without obtaining an ordinary resolution. In royal british bank v turquand 1856 6 e b 327 the company s board of directors was allowed by the memorandum of association to borrow money on behalf of the company if authorised by an ordinary resolution.