Purposive Sampling In Quantitative Research Example
The goals and techniques associated with probability samples differ from those of nonprobability samples.
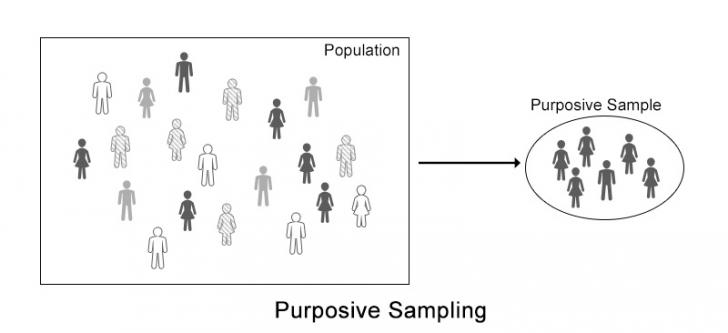
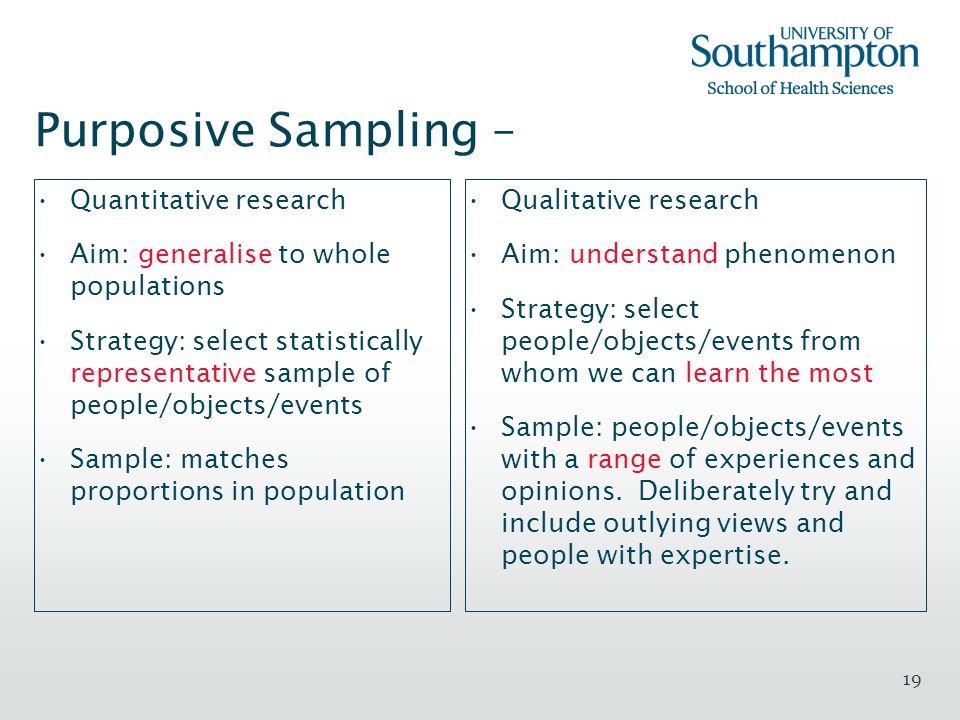
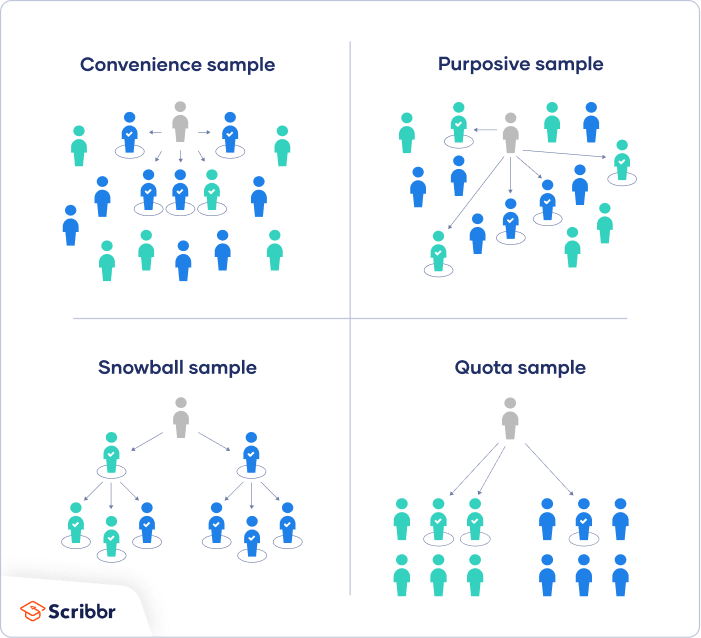
Purposive sampling in quantitative research example. Simply put purposive sampling is when a researcher chooses specific people within the population to use for a particular study or research project. Expert sampling is a form of purposive sampling used when research requires one to capture knowledge rooted in a particular form of expertise. A purposive sample also referred to as a judgmental or expert sample is a type of nonprobability sample. Purposive sampling has a long developmental history and there are as many views that it is simple and straightforward as there are about its complexity.
The reason for purposive sampling is the better matching of the sample to the aims and objectives of the research thus improving the rigour of the study and trustworthiness of the data and. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples e g when doing exploratory research quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques. It is common to use this form of purposive sampling technique in the early stages of a research process when the researcher is seeking to become better informed about the topic at hand before embarking on a study. Non probability sampling to learn more about non probability sampling and sampling.
Researchers often believe that they can obtain a representative sample by using a sound judgment which will result in saving time and money. The main objective of a purposive sample is to produce a sample that can be logically assumed to be representative of the population. Purposive sampling is a non probability sampling method and it occurs when elements selected for the sample are chosen by the judgment of the researcher. This is often accomplished by applying expert knowledge of the population to select in a nonrandom manner.
Research is a scientific process of investigation and experimentation that involves the systematic collection analysis and interpretation of data to answer a certain question or solve problem. Purposive sampling also known as judgmental selective or subjective sampling is a type of non probability sampling technique non probability sampling focuses on sampling techniques where the units that are investigated are based on the judgement of the researcher see our articles. Hence being systematic it has certain methods and. The example of sampling for a qualitative evidence synthesis presented in this article is drawn from a cochrane qualitative evidence synthesis on parents and informal caregivers views and experiences of communication about routine childhood vaccination we understood at an early stage that the number of studies eligible for this synthesis would be high.