Acute Exacerbation Of Bronchial Asthma Ncp
Extrinsic asthma usually begins in childhood and the client may be allergic to dust pollen insects mold spores smoke medications and foods.
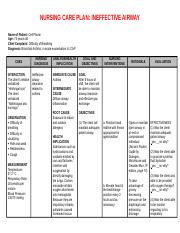
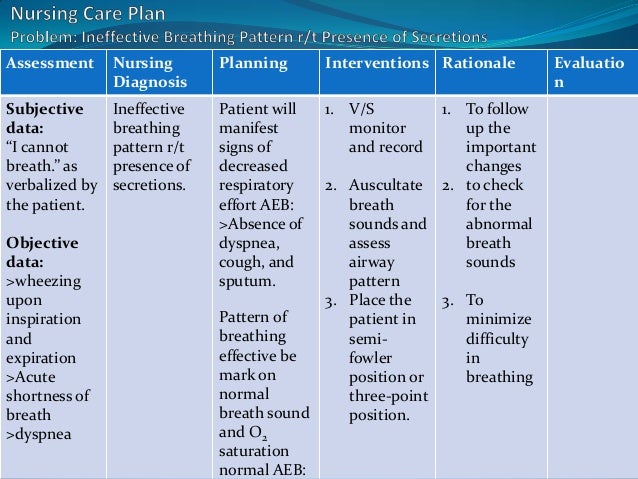
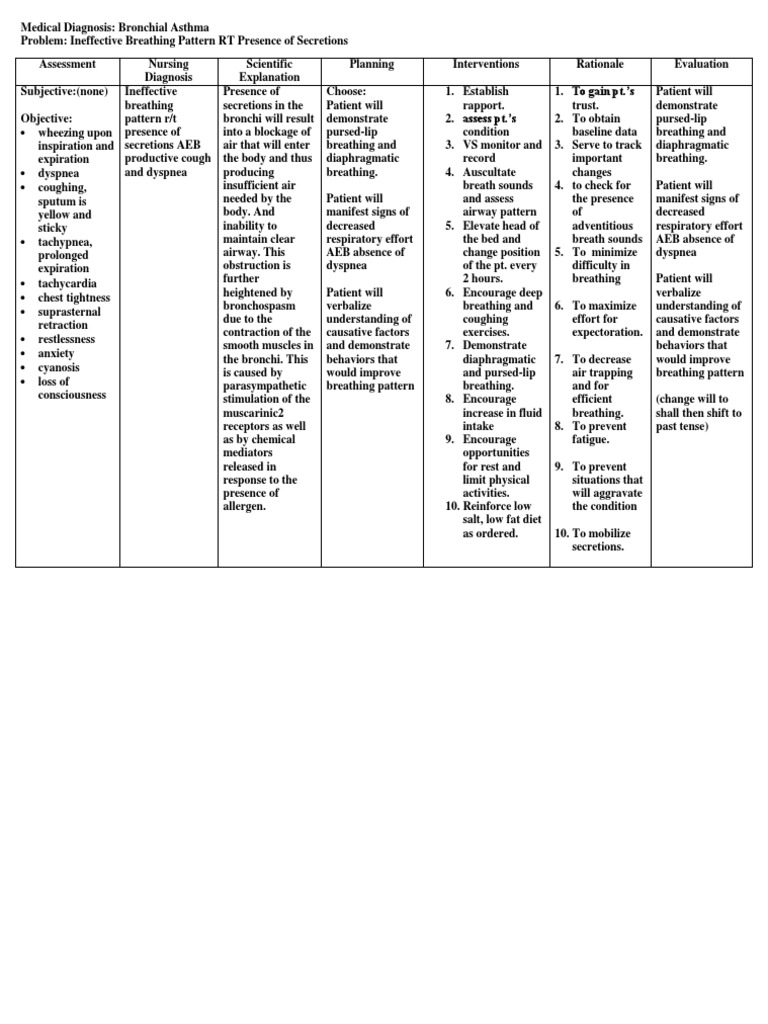
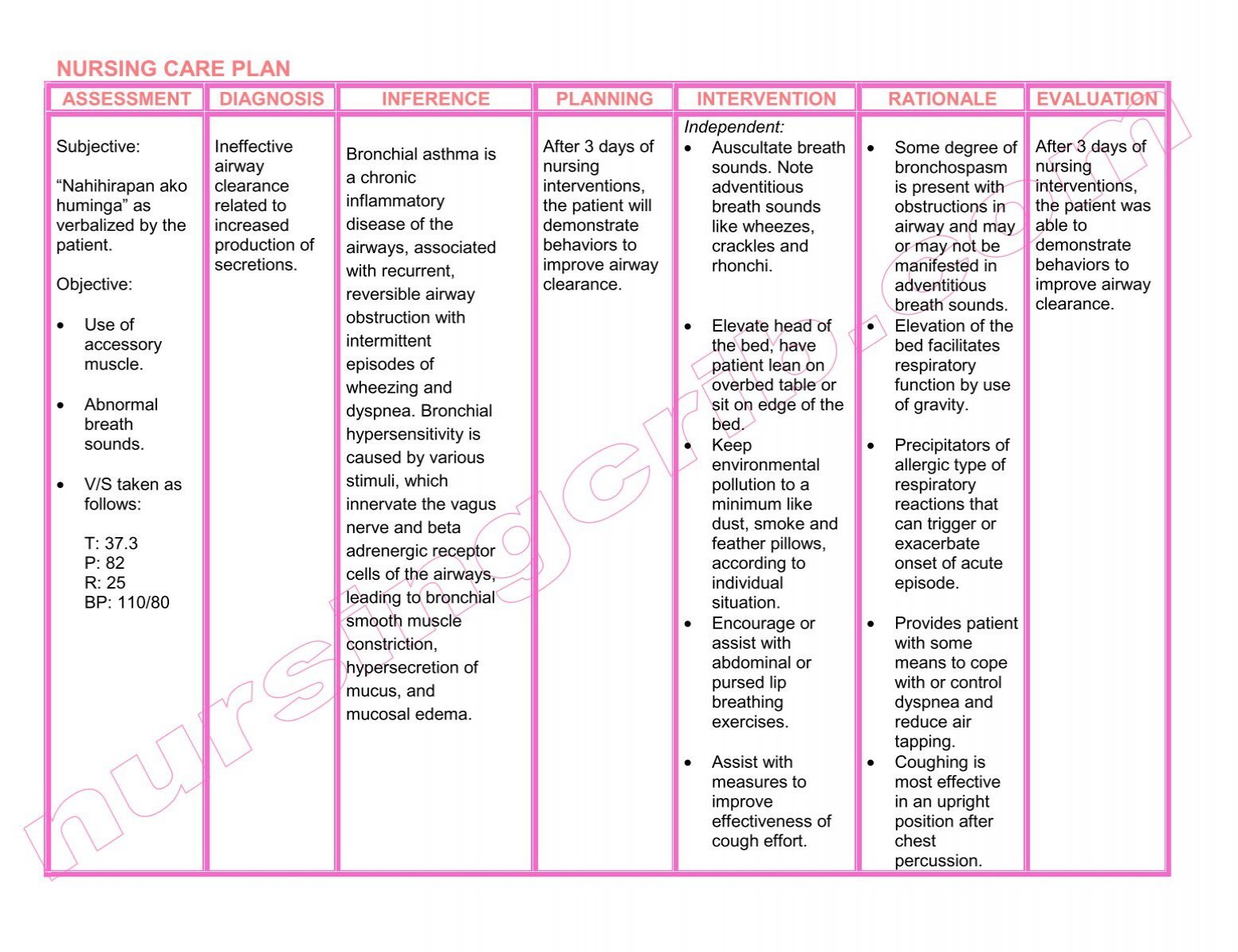
Acute exacerbation of bronchial asthma ncp. Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that causes airway hyperresponsiveness mucosal edema and mucus production. Client education asthma self management education is essential to the control of asthma and should be encouraged to all patients to take responsibility for his or her own care. Learn how to recognize the symptoms as well as potential triggers and risk factors. Patients having an asthma exacerbation are instructed to self administer 2 to 4 puffs of inhaled albuterol or a similar short acting beta 2 agonist up to 3 times spaced 20 minutes apart for an acute exacerbation and to measure peak expiratory flow pef if possible.
In this guide are eight 8 nanda nursing diagnosis for asthma nursing care plans including their nursing assessment and interventions. This inflammation ultimately leads to recurrent episodes of asthma symptoms. Asthma is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes airway hyperresponsiveness mucus production and mucosal edema resulting in. Asthma is a disorder of the bronchial airways characterized by periods of bronchospasm.
Inflammation ultimately leads to recurrent episodes of asthma symptoms. Acute exacerbation of asthma also known as an asthma attack can be a medical emergency if it s severe. The nurse obtains a set of vital signs on a client with asthma. Respirations 22 pulse 95 oxygen saturation 84 on 6 liters nasal cannula blood pressure 130 85.
Learn more about the goals related factors and rationale for each nursing interventions for asthma. Asthma the most common chronic disease of childhood can begin at any age. Patients with asthma may experience symptom free periods alternating with acute exacerbations that last from minutes to hours or days. If asthma symptoms are controlled the patient should have fewer exacerbations a higher quality of life lower costs slower progression of airway from inflammation less morbidity and lower risk of death from asthma.
Patients with asthma may experience symptom free periods alternating with acute exacerbations that last from minutes to hours or days. The patient was on appropriate drugs nebulised ipratropium bromide 0 5mg and nebulised salbutamol 5mg in normal saline 4 hourly iv hydrocortisone 100mg stat for acute management of severe asthma as according to guidelines and eventually her sob was relieved 2 3 however she was prescribed with oral prednisolone at dose as low as 30mg od for acute asthma it should be suggested to increase. Cough chest tightness wheezing and dyspnea.









.png)

.png)