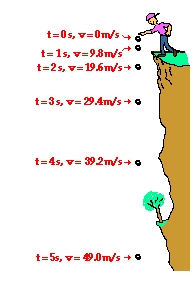Acceleration Due To Gravity Example

Its measured value varies slightly with latitude due to rotation of earth and longitude due to non spherical shape of earth and also with depth and height from the earth s surface.
Acceleration due to gravity example. Mass of earth is 5 979 10 24 kg. 3 results and discussion inspection of equation 2 shows that the free fall distance h depends linearly on the 1 2t 2. The acceleration which is gained by an object because of gravitational force is called its acceleration due to gravity its si unit is m s 2 acceleration due to gravity is a vector which means it has both a magnitude and a direction the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of earth is represented by the letter g it has a standard value defined as 9 80665 m s 2 32 1740 ft s 2. Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration of a body falling freely under the influence of the earth s gravitational pull at sea level.
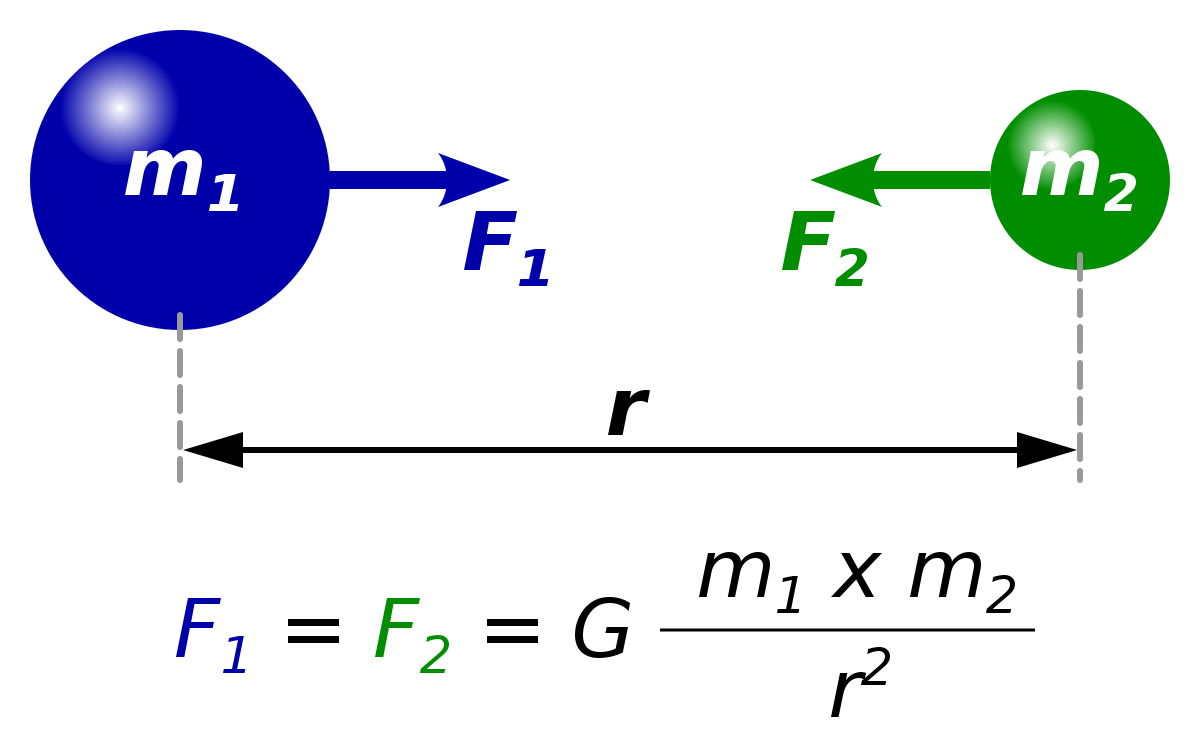
Universal gravitational constant is 6 67408 10 11 m 3 kg 1 s 2. Acceleration due to gravity formula. Mass of the body distance from the center of mass constant g. The slope is determined.
Near the surface of earth the acceleration due to gravity is approximately constant. But at large distances from the earth or around other planets or moons it is varying. Similarly you would have different values for both jupiter and pluto. Calculating the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth.
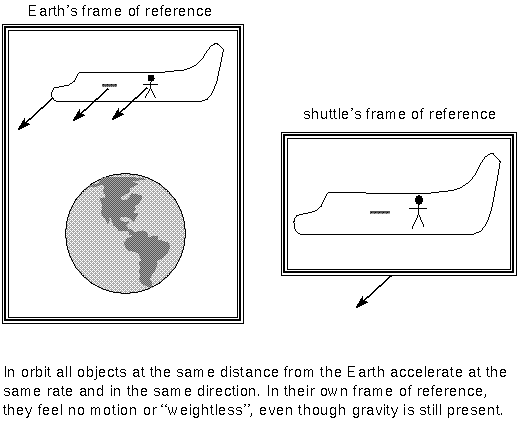
It is approximately equal to 9. Your question assumes that gravity is an example of uniform acceleration. Its value near the surface of the earth is 9 8 ms 2. 8 m s 2.
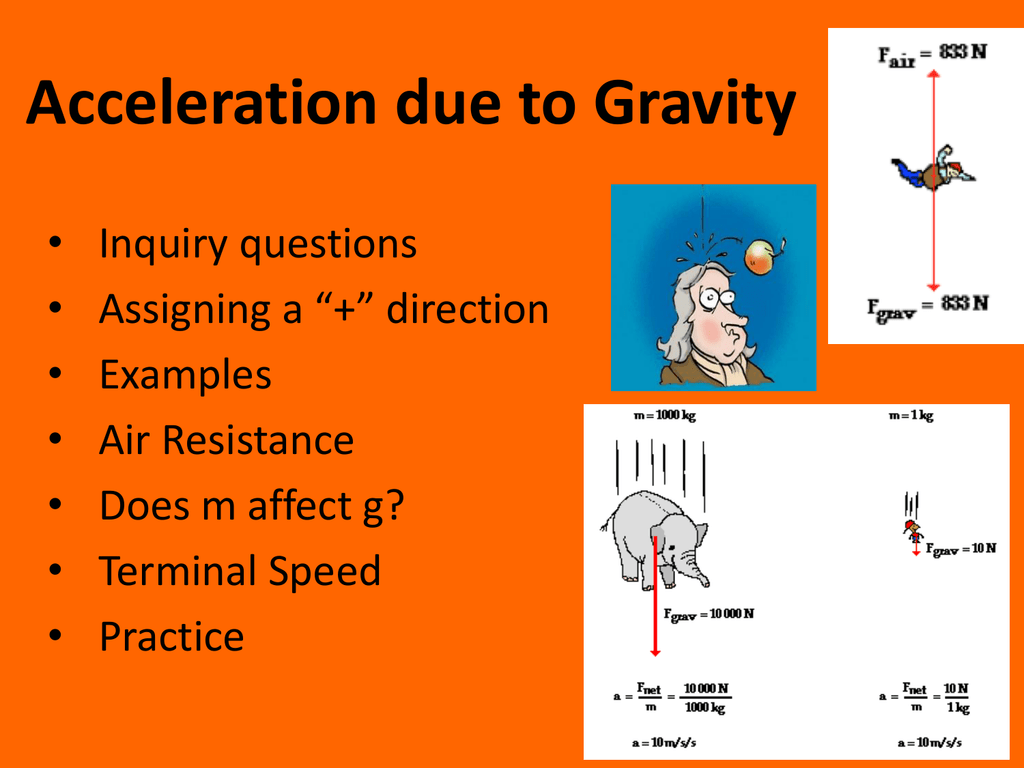
Practice questions researchers at nasa load a 100 kilogram package onto a rocket on earth. Acceleration due to gravity example. The slope of this line is acceleration due to gravity. The acceleration due to gravity depends on the terms as the following.
Radius of earth is 6 376 10 6 m. Substitute the values in the formula g 6 67408 10 11 5 979 10 24 6 376 10 6 2. In figure 1 we plot all the data in this way along with the best linear fit to the data. The above acceleration is due to the gravitational pull of earth so we call it acceleration due to gravity it does not depend upon the test mass.
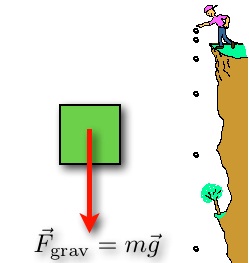
This force causes all free falling objects on earth to have a unique acceleration value of approximately 9 8 m s s directed downward. We refer to this special acceleration as the acceleration caused by gravity or simply the acceleration of gravity. Formula of acceleration due to gravity. Therefore the acceleration due to gravity g is given by gm r 2.
For example you can compare one planet to another based on their respective masses and radii. For example the acceleration due to gravity would be different on the moon as compared to the one here on earth. Here are some practice questions that illustrate this concept. Gravitational acceleration known as math g math is dependent on only a few things and one of which is not constant.