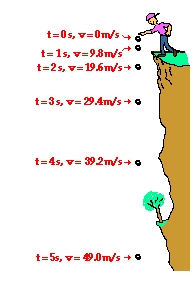Acceleration Due To Gravity Exact Value

5 98x10 24 kg and the distance d that an object is from the center of the earth.
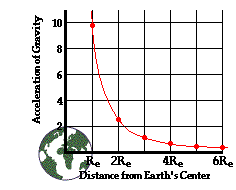
Acceleration due to gravity exact value. G gm r h 2. The gravity of earth denoted by g is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation from mass distribution within earth and the centrifugal force from the earth s rotation. Caption the acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration of a body due to the influence of the pull of gravity alone usually denoted by g. The value of g is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of.
The above acceleration is due to the gravitational pull of earth so we call it acceleration due to gravity it does not depend upon the test mass. Therefore the acceleration due to gravity g is given by gm r 2. If the value 6 38x10 6 m a typical earth radius value is used for the distance from earth s center then g will be calculated to be 9 8 m s 2. Acceleration due to gravity formula.
Formula of acceleration due to gravity. 9 806 65 m s 2. This force causes all free falling objects on earth to have a unique acceleration value of approximately 9 8 m s s directed downward. The acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration that an object experiences because of gravity when it falls freely close to the surface of a massive body such as a planet.
Where m is the mass of the gravitating body such as the earth r is the radius of the body h is the. Free falling objects are falling under the sole influence of gravity. Standard uncertainty exact relative standard uncertainty exact concise form 9 806 65 m s 2. The above equation demonstrates that the acceleration of gravity is dependent upon the mass of the earth approx.
We refer to this special acceleration as the acceleration caused by gravity or simply the acceleration of gravity. This value varies from one celestial body to. The above formula shows that the value of acceleration due to gravity g depends on the radius of the earth at its surface. In si units this acceleration is measured in metres per second squared in symbols m s 2 or m s 2 or equivalently in newtons per kilogram n kg or n kg 1.
Its value near the surface of the earth is 9 8 ms 2. Standard acceleration of gravity. Also known as the acceleration of free fall its value can be calculated from the formula.