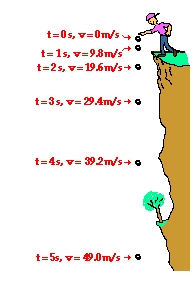Acceleration Due To Gravity Definition

The acceleration which is gained by an object because of gravitational force is called its acceleration due to gravity its si unit is m s 2 acceleration due to gravity is a vector which means it has both a magnitude and a direction the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of earth is represented by the letter g it has a standard value defined as 9 80665 m s 2 32 1740 ft s 2.
Acceleration due to gravity definition. The magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity denoted with a lower case g is 9 8 m s 2. This force causes all free falling objects on earth to have a unique acceleration value of approximately 9 8 m s s directed downward. Where m is the mass of earth and r is the radius of the earth. The standard acceleration due to gravity or standard acceleration of free fall sometimes abbreviated as standard gravity usually denoted by ɡ 0 or ɡ n is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the earth it is defined by standard as 9 806 65 m s 2 about 32 174 05 ft s 2 this value was established by the 3rd cgpm 1901 cr 70 and used to.
Near the surface of earth the acceleration due to gravity is approximately constant. Approximately 32 feet 9 8 meters per second per second. Mass of the body distance from the center of mass constant g. We refer to this special acceleration as the acceleration caused by gravity or simply the acceleration of gravity.
But at large distances from the earth or around other planets or moons it is varying. Acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of the earth consider a test mass m at a height h from the surface of the earth. F gmm r h 2. This means that every second an object is in free fall gravity will cause the velocity.
Acceleration due to gravity formula. Now the force acting on the test mass due to gravity is. Acceleration of gravity definition is the acceleration of a body in free fall under the influence of earth s gravity expressed as the rate of increase of velocity per unit of time and assigned the standard value of 980 665 centimeters per second per second called also g. When the rotational component is included as above the gravity at the equator is about 0 53 less than that at the poles with gravity at the poles being unaffected by the rotation.
For the mass attraction effect by itself the gravitational acceleration at the equator is about 0 18 less than that at the poles due to being located farther from the mass center. G 9 8 m s 2.